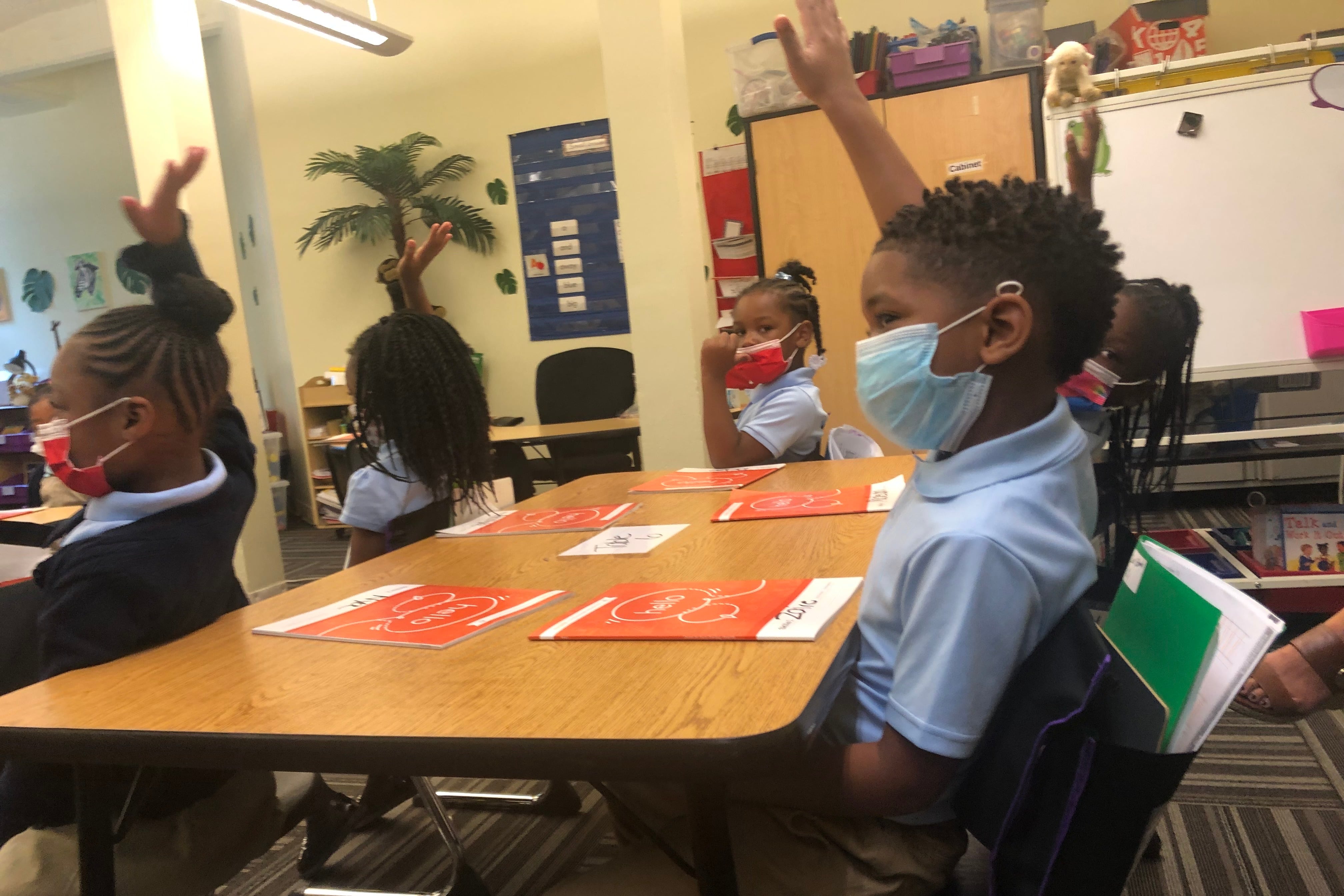
Every public school in Illinois could have full-day kindergarten by 2027, thanks to a bill passed on Friday. The bill passed 84-24 in a final house vote and is heading to Gov. J.B. Pritzker’s desk.
Under HB 2396, school districts around the state will have to offer full-day kindergarten to families with children between 4- and 6-years-old by the 2027-28 school year. School districts can continue to offer half-day kindergarten classes for families that want the option. The bill also creates a task force that will look into how school districts should implement full-day kindergarten.
First-year state Rep. Mary Beth Canty, a Democrat representing Arlington Heights and lead sponsor of the bill, applauded the general assembly for passing the bill with bipartisan support.
“I’m really proud of the work that we’ve done,” Canty said. “From the stakeholder group to advocates, to the Senate, everyone worked really hard. Not only that, I am excited because we’re helping a lot of people and that is the only reason I do this job.”
Previously, Illinois only required schools to have a half-day kindergarten program.
Early childhood education advocates have been pushing for schools to have full-day kindergarten programs. They say teachers will have more time in full-day classes to help students learn foundational skills such as the alphabet, colors, and numbers and prepare them to enter elementary school.
Canty told Chalkbeat Chicago in April that she advocated for the bill to help working families, especially working mothers who have left the workforce since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic to watch their young children.
While a majority of districts in Illinois report having full-day kindergarten, about 150 do not offer a full-day program. Some have only recently started offering it. School districts around the state such as River Forest School District 90 and Downers Grove Grade School District 58 — two wealthy districts in Chicago’s suburbs — are making the switch to full-day kindergarten this fall.
Even though the bill had bipartisan support in the general assembly, school district leaders voiced concern that creating full-day kindergarten would be expensive for school districts as they try to find space for more children and hire more staff.
The bill addresses those concerns by allowing school districts to waive transitioning to full-day kindergarten by two years if the district is funding below 76% according to the state’s evidence-based funding formula, is ranked in the top 25% of needing more capital funding, or meets a criteria set by the State Board of Education based on the task force’s recommendations.
Samantha Smylie is the state education reporter for Chalkbeat Chicago, covering school districts across the state, legislation, special education, and the state board of education. Contact Samantha at ssmylie@chalkbeat.org.